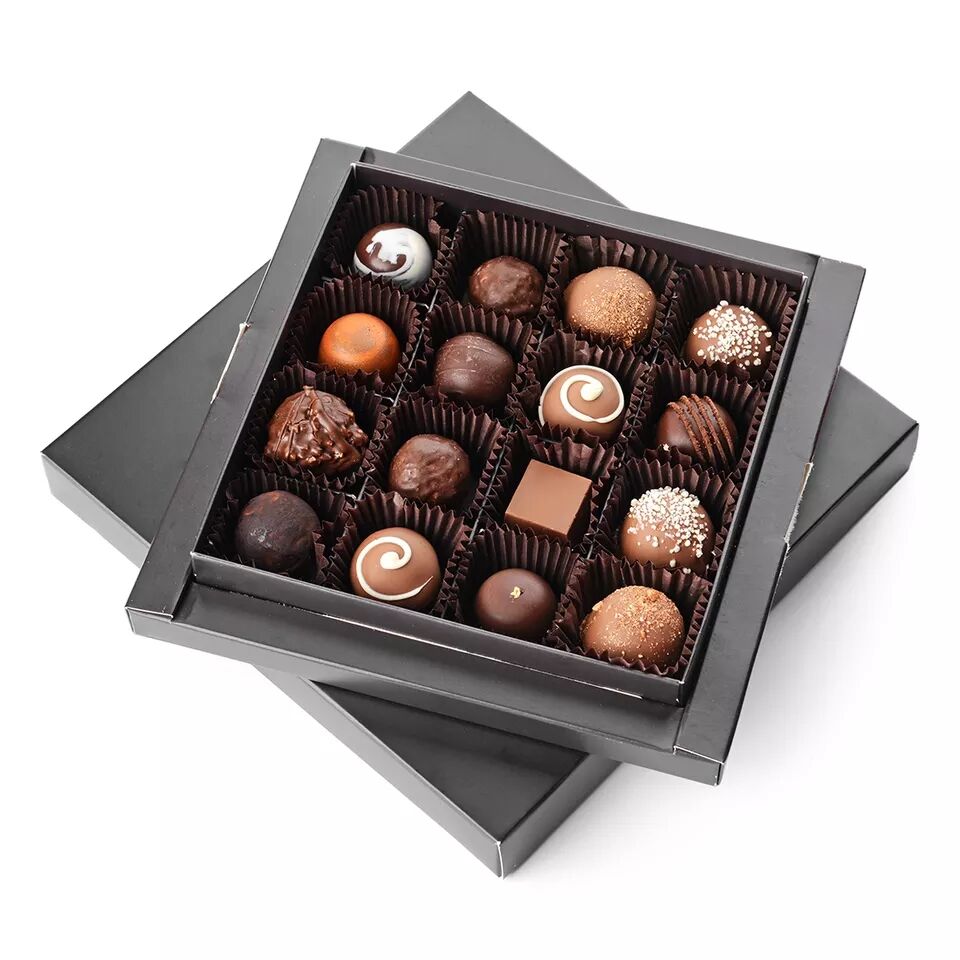
The global shift toward sustainable packaging has revolutionized how manufacturers approach product presentation, particularly in the confectionery industry. Modern consumers increasingly demand environmentally responsible packaging solutions that align with their values while maintaining the premium experience they expect from luxury chocolates. This comprehensive guide explores the evolving landscape of eco-friendly chocolate packaging, examining innovative materials, design considerations, and market trends that are reshaping how brands present their products to environmentally conscious consumers.
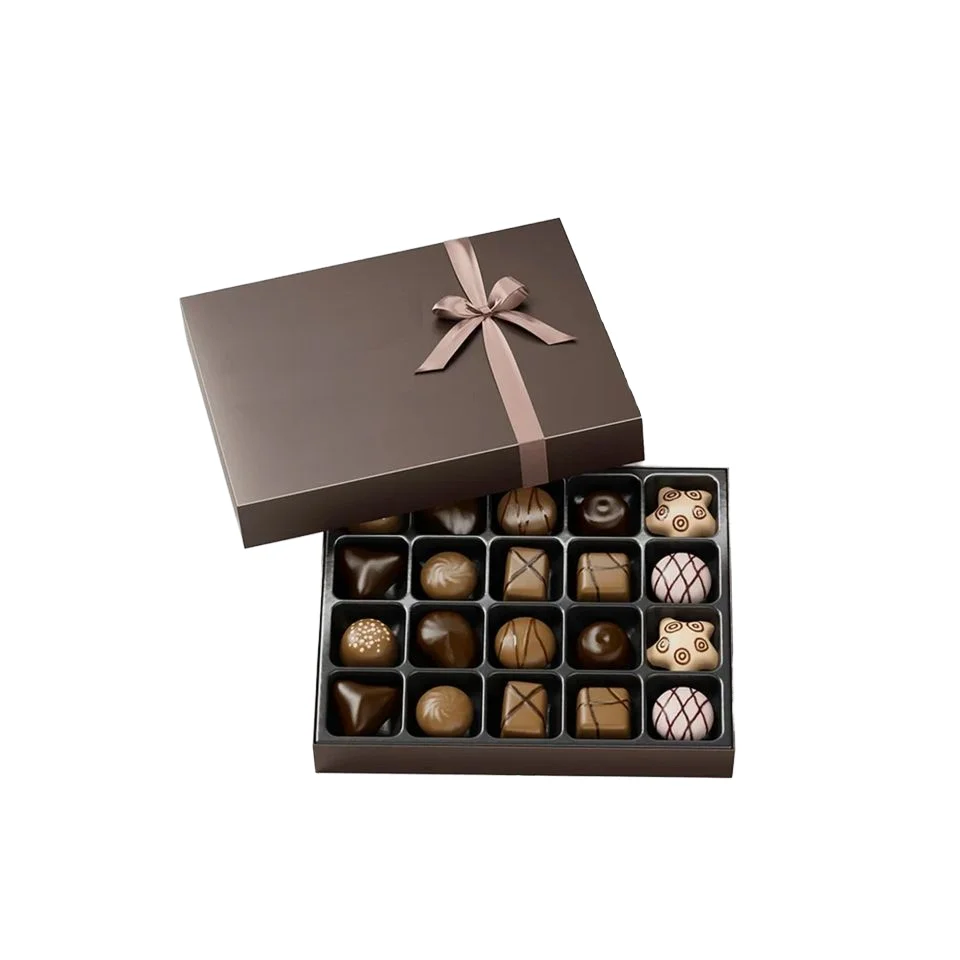

Understanding Sustainable Packaging Materials
Biodegradable and Compostable Options
The foundation of eco-friendly chocolate packaging lies in selecting materials that minimize environmental impact throughout their lifecycle. Biodegradable materials break down naturally through microbial processes, returning to the earth without leaving harmful residues. Plant-based plastics derived from cornstarch, sugarcane, and other renewable sources offer excellent alternatives to traditional petroleum-based packaging while maintaining the structural integrity required for chocolate protection.
Compostable packaging takes sustainability a step further by transforming into nutrient-rich compost under proper conditions. These materials must meet strict certification standards, ensuring they decompose within specific timeframes without releasing toxic substances. For chocolate manufacturers, compostable options include molded fiber inserts, plant-based films, and specially treated paperboard that maintains food safety standards while supporting circular economy principles.
Recycled and Recyclable Materials
Post-consumer recycled content represents another crucial component of sustainable chocolate packaging strategies. Recycled paperboard, made from recovered paper products, reduces demand for virgin materials while diverting waste from landfills. Advanced recycling technologies now enable the production of food-grade recycled materials that meet stringent safety requirements for direct food contact applications.
Design for recyclability ensures packaging components can be easily separated and processed through existing waste management systems. This approach involves careful material selection, adhesive choices, and structural design considerations that facilitate efficient recycling. Mono-material designs, which use a single material type throughout the package, significantly improve recyclability compared to multi-material composites that require complex separation processes.
Design Principles for Eco-Friendly Chocolate Boxes
Minimalist Approach and Material Optimization
Effective sustainable packaging design embraces minimalism without compromising functionality or aesthetic appeal. This philosophy involves eliminating unnecessary packaging layers, reducing material usage, and optimizing structural design for maximum efficiency. A well-designed chocolate packaging achieves protection, presentation, and sustainability through thoughtful engineering rather than excessive material application.
Material optimization techniques include right-sizing packages to product dimensions, using structural design elements for strength rather than additional materials, and incorporating multi-functional components that serve multiple purposes. Advanced packaging design software enables precise material calculations, ensuring optimal thickness, strength, and resource utilization while maintaining the premium presentation standards expected in chocolate packaging.
Functional Integration and User Experience
Sustainable chocolate packaging must deliver exceptional user experience while supporting environmental goals. This balance requires innovative design solutions that enhance functionality without compromising sustainability credentials. Integrated closure systems, built-in portion control features, and reusable design elements add value while reducing waste generation throughout the product lifecycle.
Consumer interaction design plays a crucial role in sustainable packaging success. Easy-opening mechanisms reduce frustration and potential damage, while clear disposal instructions guide proper end-of-life handling. Educational elements integrated into package design help consumers understand sustainability benefits and proper disposal methods, supporting broader environmental awareness initiatives.
Manufacturing Processes and Environmental Impact
Energy-Efficient Production Methods
Modern sustainable packaging manufacturing emphasizes energy efficiency throughout production processes. Advanced printing technologies, such as digital printing and water-based inks, significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional methods while eliminating volatile organic compounds that contribute to air pollution. LED-cured inks and coatings further minimize energy requirements while delivering superior print quality and durability.
Production facility optimization includes renewable energy integration, waste heat recovery systems, and process automation that minimizes resource waste. Manufacturers increasingly invest in solar panels, wind power, and other renewable energy sources to power their operations, creating carbon-neutral or carbon-negative production environments that align with sustainability goals.
Supply Chain Sustainability
Comprehensive sustainability approaches extend beyond individual packaging components to encompass entire supply chains. Local sourcing strategies reduce transportation-related emissions while supporting regional economies and enabling better quality control. Strategic partnerships with certified sustainable material suppliers ensure consistent access to environmentally responsible inputs while maintaining cost competitiveness.
Logistics optimization includes consolidated shipping, returnable transport packaging, and route efficiency improvements that minimize fuel consumption and emissions. Digital tracking systems provide real-time visibility into supply chain performance, enabling continuous improvement initiatives that enhance both environmental and operational efficiency.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Premium Positioning and Sustainability
Contemporary consumer research reveals strong correlations between sustainability attributes and perceived product quality, particularly in premium chocolate segments. Brands successfully positioning eco-friendly packaging as a luxury feature achieve price premiums while building stronger customer loyalty. This trend reflects evolving consumer values that prioritize environmental responsibility alongside traditional quality indicators.
Storytelling through packaging design communicates sustainability messages effectively, creating emotional connections between consumers and brands. Transparency in material sourcing, production processes, and environmental impact resonates strongly with environmentally conscious customers who seek authentic sustainability commitments rather than superficial green marketing claims.
Regulatory Compliance and Certification
Expanding environmental regulations worldwide drive chocolate manufacturers toward sustainable packaging solutions that ensure compliance across multiple markets. Emerging legislation targeting single-use plastics, extended producer responsibility programs, and mandatory recycling targets create compelling business cases for sustainable packaging investments.
Third-party certifications provide credible validation of sustainability claims, supporting marketing efforts while ensuring genuine environmental benefits. Forest Stewardship Council certification, Cradle to Cradle assessment, and biodegradability standards offer frameworks for evaluating and communicating packaging sustainability performance to stakeholders throughout the value chain.
Implementation Strategies for Brands
Transition Planning and Stakeholder Engagement
Successful sustainable packaging implementation requires comprehensive planning that addresses technical, commercial, and operational considerations. Phased transition approaches enable gradual implementation while minimizing disruption to existing operations and customer relationships. Pilot programs with select product lines or markets provide valuable learning opportunities before full-scale deployment.
Stakeholder engagement encompasses customers, suppliers, retailers, and internal teams who influence packaging decisions. Educational initiatives, feedback collection, and collaborative development processes ensure sustainable packaging solutions meet diverse stakeholder needs while achieving environmental objectives. Clear communication strategies help stakeholders understand benefits and support implementation efforts.
Cost Management and Return on Investment
While sustainable packaging materials may carry higher initial costs, comprehensive analysis reveals multiple value sources that justify investments. Operational efficiencies, waste reduction, regulatory compliance benefits, and brand value enhancement contribute to positive return on investment calculations that support business cases for sustainability initiatives.
Long-term cost projections increasingly favor sustainable options as economies of scale reduce material costs and regulatory pressures increase conventional packaging expenses. Strategic partnerships with packaging suppliers enable volume-based pricing advantages while ensuring consistent quality and supply reliability for sustainable materials.
FAQ
What makes chocolate packaging truly eco-friendly
Truly eco-friendly chocolate packaging combines sustainable materials, efficient design, responsible manufacturing, and proper end-of-life management. Key characteristics include biodegradable or recyclable materials, minimal resource usage, renewable energy production, and clear disposal guidance that enables proper waste handling by consumers.
How do sustainable chocolate boxes compare in cost to traditional packaging
Initial costs for sustainable chocolate boxes are typically 10-30% higher than conventional alternatives, but total cost of ownership often favors sustainable options when considering regulatory compliance, waste management savings, brand value enhancement, and consumer willingness to pay premiums for environmentally responsible packaging.
Can eco-friendly packaging maintain chocolate quality and freshness
Modern sustainable packaging materials and design techniques effectively protect chocolate quality and freshness. Advanced barrier coatings, moisture control systems, and structural design elements derived from sustainable materials match or exceed performance of traditional packaging while supporting environmental goals.
What certifications should brands look for in sustainable chocolate packaging
Essential certifications for sustainable chocolate packaging include Forest Stewardship Council for paper products, BPI certification for compostable materials, FDA approval for food contact surfaces, and ASTM standards for biodegradability. These certifications ensure genuine sustainability benefits while maintaining safety and quality requirements.
 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 BG
BG
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 NO
NO
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 IW
IW
 TH
TH
 MS
MS
 HY
HY